[ Instrument network instrument research and development ] Water weight metal pollution seriously endangers human health, so the detection of heavy metal elements in water is of great significance. Surface-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (SENLIBS) is a kind of elemental detection technology in water. It has the advantages of fast and high detection sensitivity and has wide practical application prospects. The existing research only reports the enhancement effect of different substrates, but the influence of the physical properties of the substrate on the detection sensitivity has not been reported.
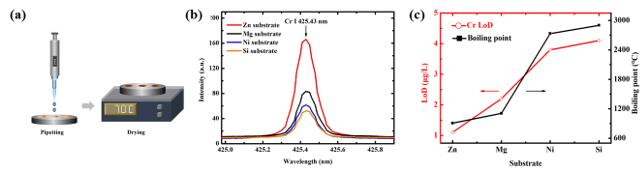
(a) Surface liquid-solid conversion (b) Cr element spectrum (c) Correlation between Cr element detection limit and boiling point
In order to study the influence of substrate physical properties on detection sensitivity in SELIBS technology, Associate Professor Guo Lianbo and his doctoral student Ma Shixiang of the Laser Advanced Manufacturing Technology Research Group of Wuhan Optoelectronics National Research Center used lining of Zn, Mg, Ni and Si. At the bottom, the relationship between the boiling point of the substrate and the detection sensitivity is established by taking two heavy metals, Cr and Pb, in the water. It is found that the lower the boiling point of the substrate, the stronger the spectral intensity and the better the detection sensitivity. Mainly because the lower the boiling point of the substrate, the smaller the ablation threshold, the larger the amount of substrate ablation, resulting in higher plasma temperature and electron density, and the final spectral intensity is enhanced, thereby improving the detection sensitivity of LIBS. At the same time, the detection limits of Cr and Pb on the optimal substrate zinc reached 1 ppb and 4 ppb, respectively, which met the national drinking water testing standards.
On May 13, 2019, the results were titled "Determination of trace heavy metal elements in aqueous solution using surface-enhanced laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy". Published in Optics Express (Vol.7, No.10), a journal of the Optical Society of America, the work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61575073).
(Original title: New progress in the study of heavy metals in water)
Machine Parts,Textile Machine,Oil Fume Purifier,Lampblack Treatment Machine
ZHEJIANG LIANKE MACHINERY CO.,LTD , https://www.zjlinkmachinery.com