


Three-phase asynchronous motor temperature rise test methods are direct load method and equivalent load method. The equivalent load method includes a reduced voltage load method and a stator superposition method. When the direct load method and the step-down load method are used, the tested motor needs to be mechanically connected with the accompanying test motor, and the stator overlap method does not require mechanical connection when performing the asynchronous motor temperature rise test, so the method is particularly suitable for difficult to There is no temperature rise test for a suitable drag motor such as a high-voltage vertical asynchronous motor, an asynchronous motor with a super-capacity capacity, and a low-speed asynchronous motor without a suitable companion test motor. The temperature-rise test of the overlapping frequency method can also reduce the assembly time of the assembly and reduce the energy consumption during the test. The experimental principle is as follows:
Adding the two frequencies to the tested motor simultaneously results in a mixed rotating magnetic field in the air gap of the asynchronous motor. In the air gap, the velocity and amplitude of the synthetic magnetic field are constantly changing. Due to the speed change, the inertia of the rotor itself and the limitations of wind wear, the average speed is similar to the synchronous speed, and the rotor is constantly changing the acceleration or deceleration state. The test circuit is shown in Figure 1.
The frequency-doubled temperature rise test uses two sets of power supplies, the main power supply and the secondary power supply. Both sets of power are generated by a synchronous generator. The main power synchronous generator coils are combined into a Y-type, and the secondary power synchronous generator coil is turned on, and is connected in series with the main power coil to form a main circuit of the stacked power supply to supply power to the tested high voltage motor. The rated current of the auxiliary power generator shall not be less than the rated current of the tested motor, and the voltage level shall be the same as the tested motor.
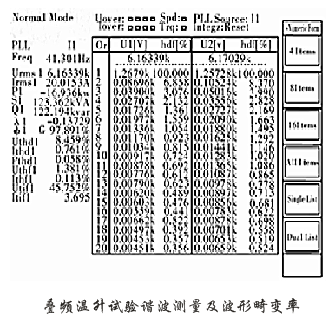
The mains frequency is the rated frequency. For a 50Hz motor, the frequency of the auxiliary power is between 38Hz and 42Hz. The main power supply voltage is the same as the rated voltage of the tested motor to ensure that the tested motor runs at the rated voltage; the voltage level of the sub power supply should be the same as the Un of the tested motor. Adjust the excitation of the auxiliary power generator to ensure that the tested motor is tested for temperature rise under rated current and rated voltage. During the loading process, the main power supply voltage must be adjusted at any time so that the terminal voltage of the tested motor is rated. The operation interface of Fig. 2 is the motor cascade frequency temperature rise test of a high-voltage asynchronous motor of a domestic motor company. Table 1 shows the test data and related waveforms of this test.
Agricultural Trolley,Flower Transport trolley,Adjustable Agricultural Trolley,Agricultural Flower Trolley
Dalian CS Logistics Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.dlcsems.com